GCCs in India are increasingly emerging as hubs of excellence for innovation and digital transformation, enhancing their significance in the value chain. Key drivers of this growth include software exports, a highly skilled tech workforce, expansion into tier-2 cities, government backing, and improving infrastructure. These factors collectively contribute to India’s thriving GCC market, solidifying its position as a pivotal player in the global business landscape.
What are GCCs?
GCCs, also recognized as global in-house centers or captives (GICs), are offshore entities strategically established by companies to deliver a spectrum of services to their parent organizations. Functioning as internal components within the global corporate framework, these centers provide specialized capabilities, including IT services, research and development, customer support, and various other business functions.
This concept originated in the early 1990s with the establishment of offshore divisions by major multinational corporations such as General Electric, Texas Instruments, Citigroup, and American Express.
India’s GCC Market Outlook to 2030
GCCs are the backbone of India’s IT and business services industry. A report by global consultancy EY predicts that India’s GCC market could reach US$110 billion by 2030, up from US$46 billion at present. Another report, the “GCC – India redefining the globalization blueprint”, estimates an increase in market size of over 33 percent, to reach US$60 billion by FY 2025.
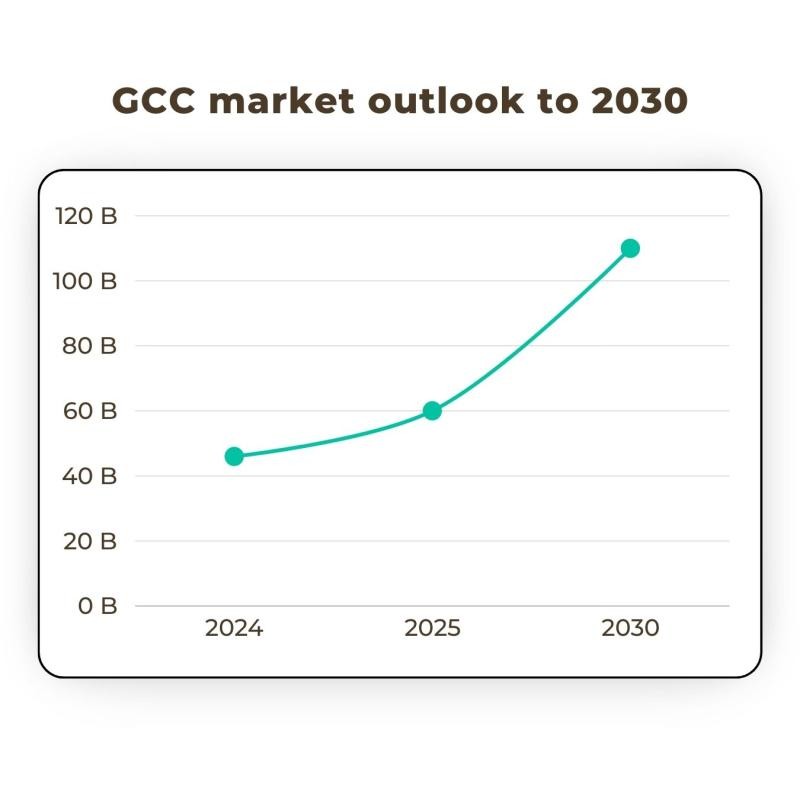
Market size and growth drivers
As of 2022, India commands a substantial 55 percent share in the world’s operational GCC centers. Projections indicate that by 2025, India will host around 320 new GCCs, marking the foray of numerous companies into establishing their inaugural global centers abroad.
The tally of GCCs in India stands at 1,580 as of 2023, poised to exceed 1,900 by 2025 and potentially reach 2,400 by 2030, with a maximum ceiling of 2,550 based on India’s capabilities. Currently, India is set to integrate 115 new GCCs annually, a notable surge from the present rate of 70 per year. This prolific growth positions India as an eminent global hub for technology and services.
The surge in GCCs in India is predominantly steered by engineering and R&D services, contributing a substantial 56 percent to the total revenue share. This momentum is fueled by India’s adept talent pool, a conducive business and policy environment, and advancing infrastructure.
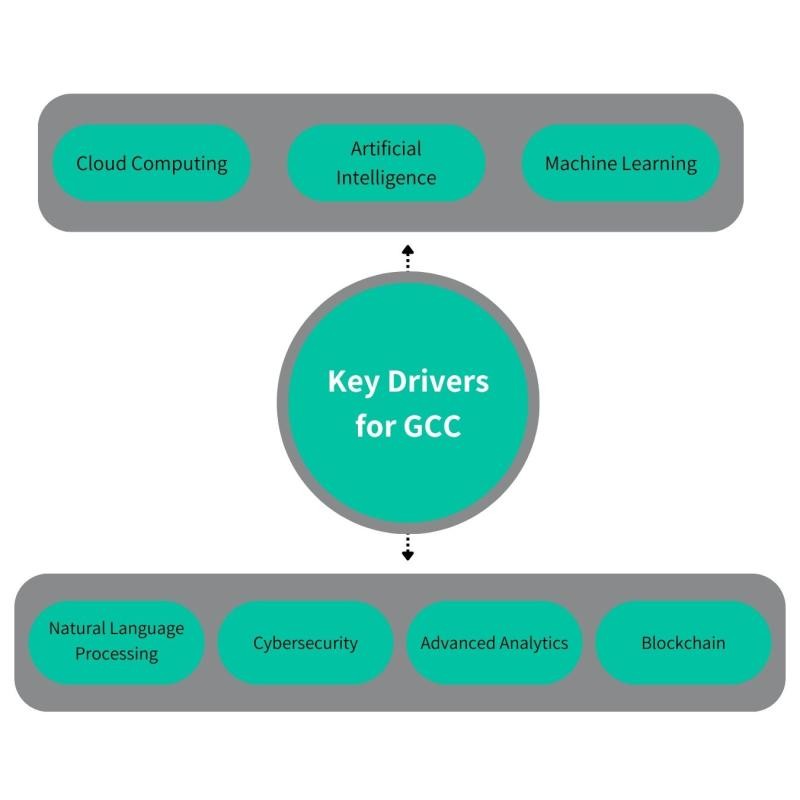
Within India, GCCs function as pivotal technology hubs for their headquarters, specializing in areas such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and natural language processing (NLP). They also delve into emerging domains like cybersecurity, advanced analytics, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT). These GCCs play a critical role in spearheading exploration into cutting-edge technologies like Web 3.0, Digital Twins, and the Metaverse as part of their parent organizations’ innovation initiatives.
The workforce within the GCC industry in India is anticipated to grow from the current 1.9 million to approximately 4.5 million individuals. The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) from 2019 to 2023 stands at an impressive 11 percent, projected to accelerate to 14 percent from 2023 to 2030. Furthermore, the cost per full-time equivalent (FTE) is forecasted to rise from the current US$29,100 to US$37,760 by the year 2030.
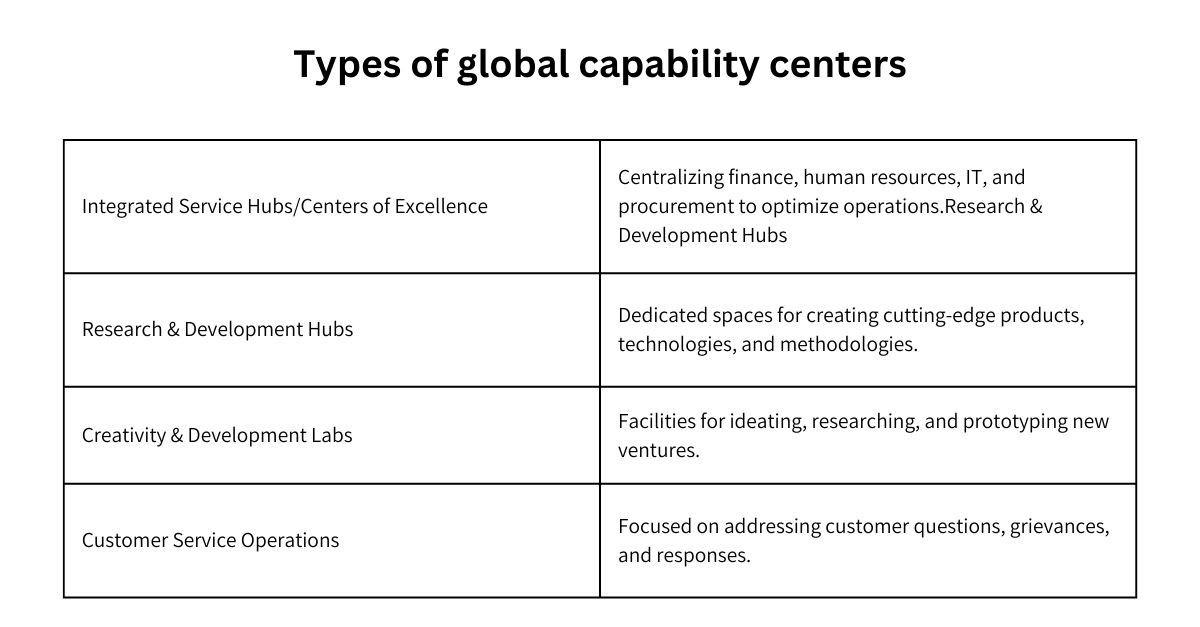
Types of Global Capability Centers
Global capability centers can be of various types. The below table lists some common types of GCCs.
Currently, R&D services dominate with a commanding 56 percent share of the total GCC revenue. Looking ahead, a significant chunk of GCC earnings is poised to emanate from ER&D and digital engineering. Forecasts indicate a robust Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of around 20 percent for these sectors, underscoring a formidable upward trajectory in their impact on GCC revenues.
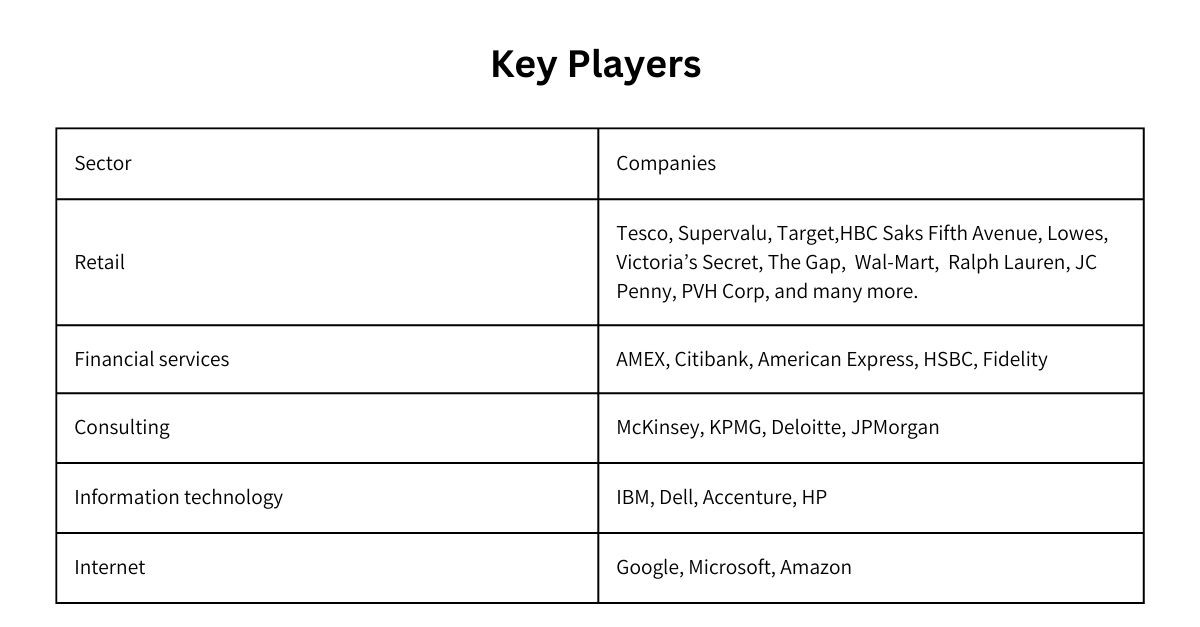
Key Players
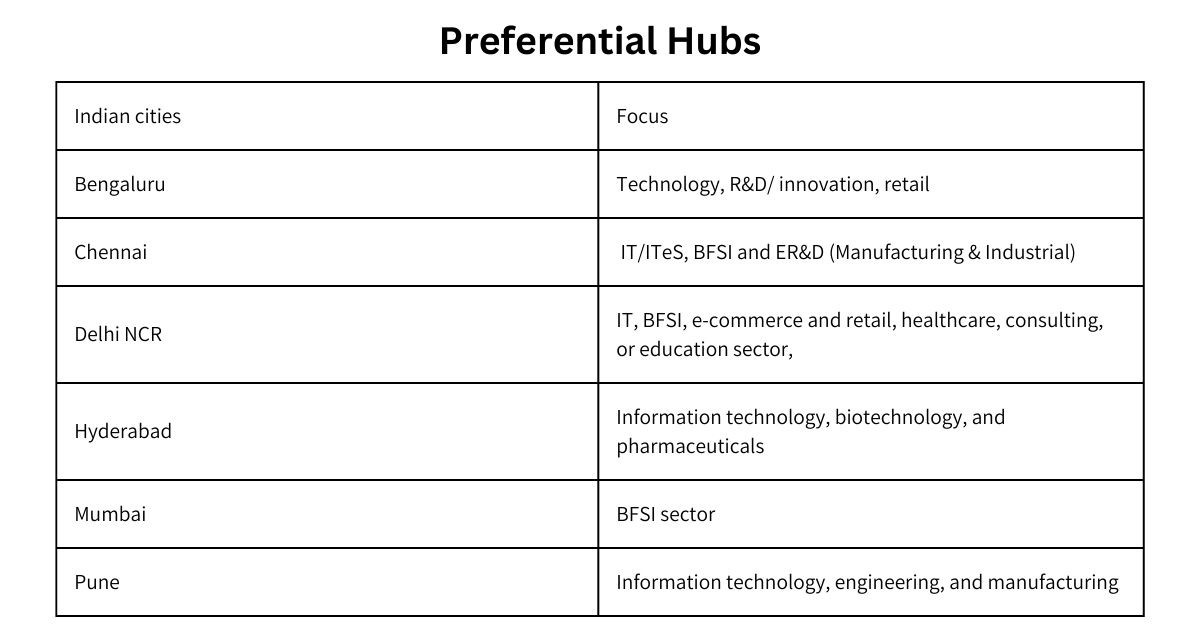
Preferential Hubs
Six premier Indian locations stand out as ideal settings for the establishment of global capability centers. These locales share key attributes such as robust infrastructure, the presence of industry leaders, access to a skilled talent pool, and a supportive ecosystem encompassing education, regulations, tax policies, research, and mobility.
Key trends in the GCC/GIC sector in 2024
Prominent trends shaping the GCC sector this year encompass:
-
- The establishment of Centers of Excellence (CoEs) in critical domains like AI, cloud computing, engineering, data analytics, and cybersecurity.
-
- A strategic shift from being a ‘cost center’ to evolving into a ‘profit center,’ with a primary focus on generating new revenue streams.
-
- Business functional expansion into areas such as legal, marketing, and procurement, leading to increased investment allocations to support these burgeoning growth sectors.
-
- A heightened emphasis on Employee Value Proposition (EVP), incorporating organizational culture, nature of work, rewards, and compensation. This ensures a more comprehensive approach to attracting and retaining top-tier talent.

